Question 1
Metal Q displaces metals T and U from their oxides but does not displaces metal R. Metal T displaces U form its oxide. Arrange the metals according to their reactivity starting with the strongest reducing agent.
Answer
R - Q - T - U
Question 2
Chlorine gas can be prepared in the laboratory using the following two methods;
Solid substance X and concentrated Hydrochloric acid
Solid substance X and concentrated Hydrochloric acid
- Name the solid substance X
- What is role of concentrated sulphuric acid in the reaction?
- State how dry chlorine gas is collected.
Answer
- substance X - Manganese (iv) Oxide (MnO4)
- It react with Sodium Chloride to produce Hydrogen Chloride which inturn reacts with Manganese (iv) Oxide to produce Chlorine gas.
- It is collected by downward delivery since it is denser than air.
Question 3
A white crystalline solid Q when heated to forms a brown gas, colourless gas that relights a glowing wooden splint and a yellow residue which turns white on cooling. Aqueous solution of Q forms white precipitate which dissolves excess aqueous ammonia solution to form a colourless solution P.
- Write the name and chemical formulae of complex ion in solution P.
Name;
Chemical formula; - State the observation made when the aqueous solution of P is reacted with few drops of sodium hydroxide.
Answer
-
Name; - Tetra anime zinc (ii) ions
Chemical formula; - [Zn(NH3)4]2+ - White precipitate is formed.
Question 4
Define term Lattice energy.
Answer
Lattice energy - Energy change when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from its' constituent ions in gaseous state.
Question 5
The reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen releases energy. A student drew the reaction profile for the reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
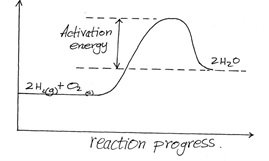
State two errors made when drawing the reaction profile.
Answer
1. Products should be at a lower energy than reactants.
2. Labelling of the Y - axis (Energy in Kj/mol)
3. The activation energy should be from the reactants to the peak.
2. Labelling of the Y - axis (Energy in Kj/mol)
3. The activation energy should be from the reactants to the peak.
